Fileless click-fraud malware
It’s
holiday today. Lots of kids will be opening presents
and playing with new toys. However,
I’m
here as every week. I’m reading and writing about malware. I read
the the
evolution of the fileless click-fraud malware Poweliks
last week and I wanted to read it deeply and write about it. I think
this is the best way to learn and get knowledge about this kind of
malware. I’ve
already written about fileless
malware forensics.
Therefore, I know a little bit how these malware work. Today,
I’m going to deep down in tricks and innovations of the
fileless
click-fraud
malware
Poweliks.
The
first innovation is the registry
protection.
It’s
a trick used by this
fileless
malware which
inserts
an extra registry subkey. This
subkey contains an entry with
the 0x06 byte and the 0x08 byte, which
are not Unicode printable character sets, thus it is
difficult to read
and delete properly. For
instance, we won’t be able to read and delete this subkey with the
default Windows Registry Editor. Therefore, we’ll need another
registry tool to handle these special characters. In
addition, administrative
users
won’t be able to delete this subkey thus permissions must be
modified in order to delete the unreadable entry.
 |
| Extra registry subkey to protect Poweliks in memory |
Another
innovation is the CLSID
hijacking.
A
CLSID or Class Identifier is a globally unique identifier that is
used to represent a specific instance of a program. It
allows operating systems and software to detect and access software
components without identifying them by their names. CLSID
hijacking is used by fileless malware to implant DLLs. These DLLs
will be launched legitimately by trusted
and whitelisted processes
such as
explorer.exe,
chrome, iexplorer, etc.
The
third trick or innovation is the fileless
persistence.
Lots
of malware hide a malicious executable on the compromised computer
which is then executed. However, fileless malware don’t store
anything on disk. They
save malicious code in the Windows Registry which
is executed to load malicious DLLs. For instance, the fileless
malware Poweliks executes rundll32.exe with several parameters, one of them is a JavaScript code used to load the malware into the
memory.
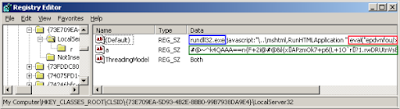 |
| Loading JavaScript code through the registry |
Most
fileless malware need an exploit to insert the code into the Windows
Registry. For instance, Poweliks was using a Windows zero-day
exploit for privilege escalation.
Thanks
to this zero-day vulnerability, Poweliks run regedit to insert the
malicious code into the
Windows Registry. In addition, Poweliks was using this vulnerability
to run a batch file.
Finally,
how
these malware put
the money in the pocket?
A fileless click-fraud malware is going to click lots of ads.
However, the victim doesn’t know the computer is clicking too many
ads. Meanwhile,
attackers generates money to be paid by the advertiser to the
publisher. In addition, this kind of malware can also download more
malware. For instance, one of the websites visited by Poweliks
resulted in Cryptowall being installed on the computer.
 |
| Poweliks advertisement request |
To
sum up. It’s holiday. There are lots of gifts and presents today. I
wish you many and lots this year. However, open the eyes! Be caution!
Protect your systems!!
Have
a nice day!






Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire