Cisco Nexus FabricPath
Configuring
the Spanning-Tree
Protocol (STP) is mandatory in high scalable networks because
we’ll have lots of switches and we'll have to build loop-free
topologies. However, STP sets links in blocking state to make
loop-free topologies. Therefore, some links are not used and we can’t
send traffic for more than one link at a time. Maybe, you are
thinking about etherchannels or LACP links to send traffic for
more than one link at a time but this technology only works between
two switches thus it won’t allow uplinks to more than one device at
a time.
An
evolution of EtherChannels is Cisco
Nexus vPC, which allows uplinks to two different switches to
be active at the same time, but this technology is great for a server
and not for scalable networks because it only allows two upstream
switches per vPC. Therefore, if STP, EtherChannels or vPC is not
great for high scalable networks, what technology fits this
requirement? Cisco Nexus FabricPath is one of the best
protocol for topologies where there are many switches with
north-south and east-west traffic.
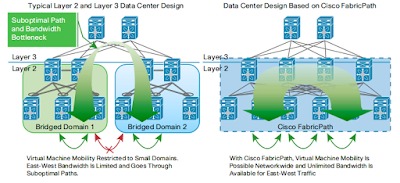 |
| Comparison Between Traditional Data Center Design and a Cisco FabricPath Design Using the Same Networking Equipment |
Cisco
Nexus FabricPath is a proprietary protocol which has enhanced the
TRILL (Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links) standard. The
aim of Cisco FabricPath is to replace STP to overcome the STP
limitations. Hence, the Cisco protocol is going to simplify the
topology and the configuration as well as maximizes bandwidth
availability using ECMP (Equal Cost Multi-Pathing). In addition, as
STP is not required, each switch is going to have its own Layer 2
topology which offers ECMP and loop prevention by using TTL.
We are
used to configuring dynamic
routing protocols, such as OSPF or BGP, for Layer 3
topologies but it’s amazing how these protocols can also help us to
build Layer 2 topologies with loop-free connectivity like IS-IS does
with Cisco FabricPath. It’s easy to understand, as dynamic routing
protocols use IP addresses to build the routing table for Layer 3
topologies, dynamic routing protocols can also use MAC addresses to
build loop-free Layer 2 topologies with load-balancing traffic using
ECMP.
Most
network engineers already know how to configure STP and Cisco
FabricPath seems challenging because of IS-IS configuration. However,
we don’t have to configure IS-IS because it’s automatically
configured when Cisco FabricPath is enabled. This is an advantage but
I have to say there is a disadvantage because STP only works at
control plane but FabricPath works at control and data plane thus
there is a new FabricPath header.
Actually,
Cisco FabricPath uses a MAC-in-MAC encapsulation where the Inside MAC
(iMAC) is the Classical Ethernet MAC address and OMAC is the Outside
MAC address for the FabricPath domain. What’s more, as FabricPath
frame is larger than the Classical Ethernet frame, due to the extra
header, FabricPath switches should use jumbo frames or have the MTU
increased.
 |
| FabricPath Frame Encapsulation |
Did
you know TRILL or Cisco FabricPath for scalable networks?





Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire