AWS Key Management Service
The
first time I took part in a project about PCI-DSS
Compliance, I was impressed about
the importance of Key Management to encrypt and decrypt credit or
debit card information into the PCI-DSS
Compliance. The
Key Management process is important because PCI-DSS
requires credit or debit card information is encrypted with a Data
Encryption Key (DEK) and
this key, DEK, has to be encrypted with a Key Encryption Key (KEK).
In addition, DEK and KEK can’t be saved in the same server and
they have to be rotated periodically. There are different ways to
comply this
requirement. AWS KMS is one of them and I’m
going to write about it
today.
AWS
KMS or AWS
Key Management Service is
a fully managed
service which helps us to control encryption keys that we used to
encrypt data. This is a service integrated into other AWS services
thus it’s useful if we want to protect
data of other AWS
services. AWS KMS is also integrated into
AWS CloudTrail
for logging and auditing encryption keys
which is mandatory in many standards like PCI-DSS. Thanks
to this centralized service, we can save Keys easily as
well as configuring automatic key rotation,
logging and auditing.
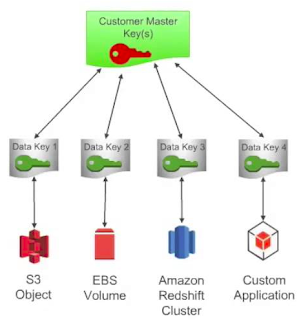 |
| How AWS Services Integrate with AWS Key Management Service |
If
we want to store encrypted data into the
Amazon S3, we can use the Server-Side
Encryption with AWS KMS-Managed Keys (SSE-KMS)
architecture which uses an envelope key to
encrypt each object’s data encryption key and this allow us
greater control of who can decrypt data,
and provides an audit log of key usage. On the other hand, we can use
the Server-Side Encryption
with Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3)
architecture where S3 encrypts the object
with a unique data encryption key and this data encryption key is
itself encrypted with a master key that the S3 service rotates
annually. Another
architecture is the Server-Side
Encryption with Customer-Provided Keys (SSE-C)
where we use our own key which is
managed by
ourself thus S3 never stores this key.
 |
| How SSE-S3 with AWS Managed Keys Works |
All
of these previous architectures
encrypt data from the Server-Side which
means data are encrypted after sending it to Amazon S3 thus
AWS always encrypts data. However,
if we want to
encrypt data before sending it to Amazon S3 we can use the
Client-Side Encryption
architecture where we encrypt our data and we manage our own keys.
There are two options of using Client-Side
Encryption. The first option is using an AWS
KMS-Managed Customer Master Key (CMK)
where we first
send a request to AWS KMS for a randomly generated data encryption
key that we can use to encrypt our object data. The second option is
using a Client-Side Master Key
where keys an unencrypted data are never sent to AWS.
 |
| Client-Side Encryption |
In
addition to storing
encrypted information into the Amazon S3, AWS KMS
is also integrated
with other AWS services such as Amazon
EBS for encrypting volumes, Amazon
Redshift for encrypting data warehouse
and Amazon
RDS for encrypting databases. What’s
more, if we want to use a Hardware Security Module for crypto
operations and key storage, we can also used AWS
CloudHSM.
 |
| Comparison of key management options |
We
can use a Key
Management Service for PCI-DSS compliance but we can also use this
kind of service when we have to store keys for any other reason like
Netflix
does who uses AWS CloudHSM for storing passwords.
How
do you manage your keys?





Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire